
237
19–22 APRIL, 2017, BARCELONA, SPAIN
S22: STONES
Moderators: Juan P. Corbetta (Argentina), Henri Lottmann (France)
ESPU Meeting on Saturday 22, April 2017, 10:20–11:02
10:20–10:23
S22-1 (PP)
★
IMBALANCE IN URINARY PROTEOGLYCANS
AND THE INSULIN GROWTH FACTOR (IGF) AXIS
IN CHILDREN WITH UROLITHIASIS
Larisa KOVACEVIC
1
, Hong LU
1
, Joseph A. CARUSO
2
, Ronald THOMAS
3
and Yegappan LAKSHMANAN
1
1) Children’s Hospital of Michigan, Pediatric Urology, Detroit, USA - 2) Institute of Environmental Health Sciences,
Wayne State University, Proteomics, Detroit, USA - 3) Children’s Hospital of Michigan, Wayne State University, Statistics,
Detroit, USA
PURPOSE
Based on the role of the extracellular matrix (ECM) in the Randall plaque formation, we aimed to
identify and quantify ECM proteins in the urine of children with urolithiasis (RS) using a proteomic
approach.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Prospective, controlled, pilot study of pooled urine from RS (N=30, 24 females, mean age
12.95±4.03 years) versus age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HC), using mass spectrom-
etry. Relative protein abundance was estimated using spectral counting. The criteria for protein
selection were: 1) ≥5 spectral counts; 2) ≥2-fold difference in spectral counts; and 3) ≤0.05 p-value
for the Fisher’s Test. Results were confirmed by ELISA.
RESULTS
We found 36 (15.7%) ECM proteins out of 229 that met the above criteria. Significant differences
between RS and HC were found among two proteoglycans and four insulin growth factor (IGF)
proteins (Table). Significant increase in the urinary excretion of IGFBP4 in RS versus HC was
confirmed by ELISA (p=0.001).
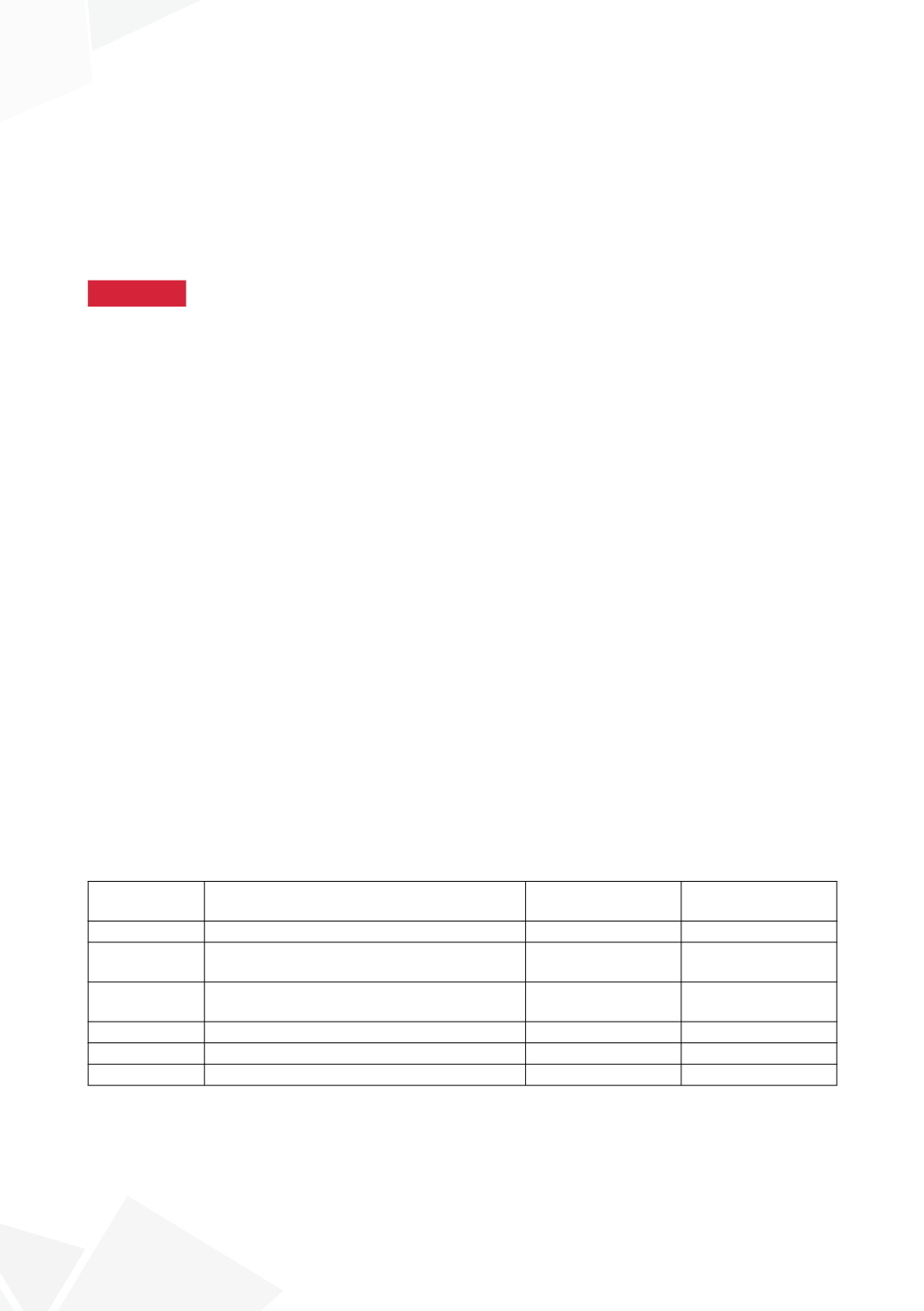
Accession
Number
Protein
Assigned peptides Ratio
(Patient/Control)
PRG4
Proteoglycan 4
38 (5)
7.6*
SDC1
Heparan sulfate proteoglycan
(Syndecan 1)
5 (50)
0.1*
IGF2R
Cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate
receptor
2 (13)
0.15*
IGFBP1
Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 1 8 (0)
Unique
IGFBP4
Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 4 17 (4)
4.2*
IGFBP6
Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 6 49 (2)
24.5*
*P<0.01
CONCLUSIONS
Alteration in proteoglycans and the IGF axis appears to have a significant role in the mechanism of
urolithiasis, likely by modulating ECM biosynthesis. Further understanding of their roles in urolithi-
asis may aid in generation of novel therapeutic approaches.









