
233
19–22 APRIL, 2017, BARCELONA, SPAIN
09:17–09:20
S21-2 (PP)
★
IMPROVED SLEEP QUALITY FOLLOWING
ADENOTONSILLECTOMY (TA) IS ASSOCIATED WITH
ENURESIS (NE) RESOLUTION IN CHILDREN WITH
SLEEP‑DISORDERED BREATHING (SDB)
Larisa KOVACEVIC
1
, Hong LU
1
, Myreia DIAZ-INSUA
2
and Yegappan LAKSHMANAN
1
1) Children’s Hospital of Michigan, Pediatric Urology, Detroit, USA - 2) Henri Ford Hospital, Urology, Detroit, USA
PURPOSE
We have previously reported that TA leads to complete resolution of NE in about 50% of children
with SDB, but the mechanism is not entirely clear. In this study we assessed the effect of TA on
sleep quality, night time urinary volume (NUV) and secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and
brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) in children with NE and SDB.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Prospective pilot study of 40 children 5-18 years of age diagnosed with SDB (snoring and obstructive
sleep apnea syndrome, OSAS) on polysomnography, and monosymptomatic primary NE (MPNE)
requiring TA for upper airway obstruction release. Arousal score, nocturia, NUV, and plasma levels
ADH and BNP were measured pre and 1 month post-surgery.
RESULTS
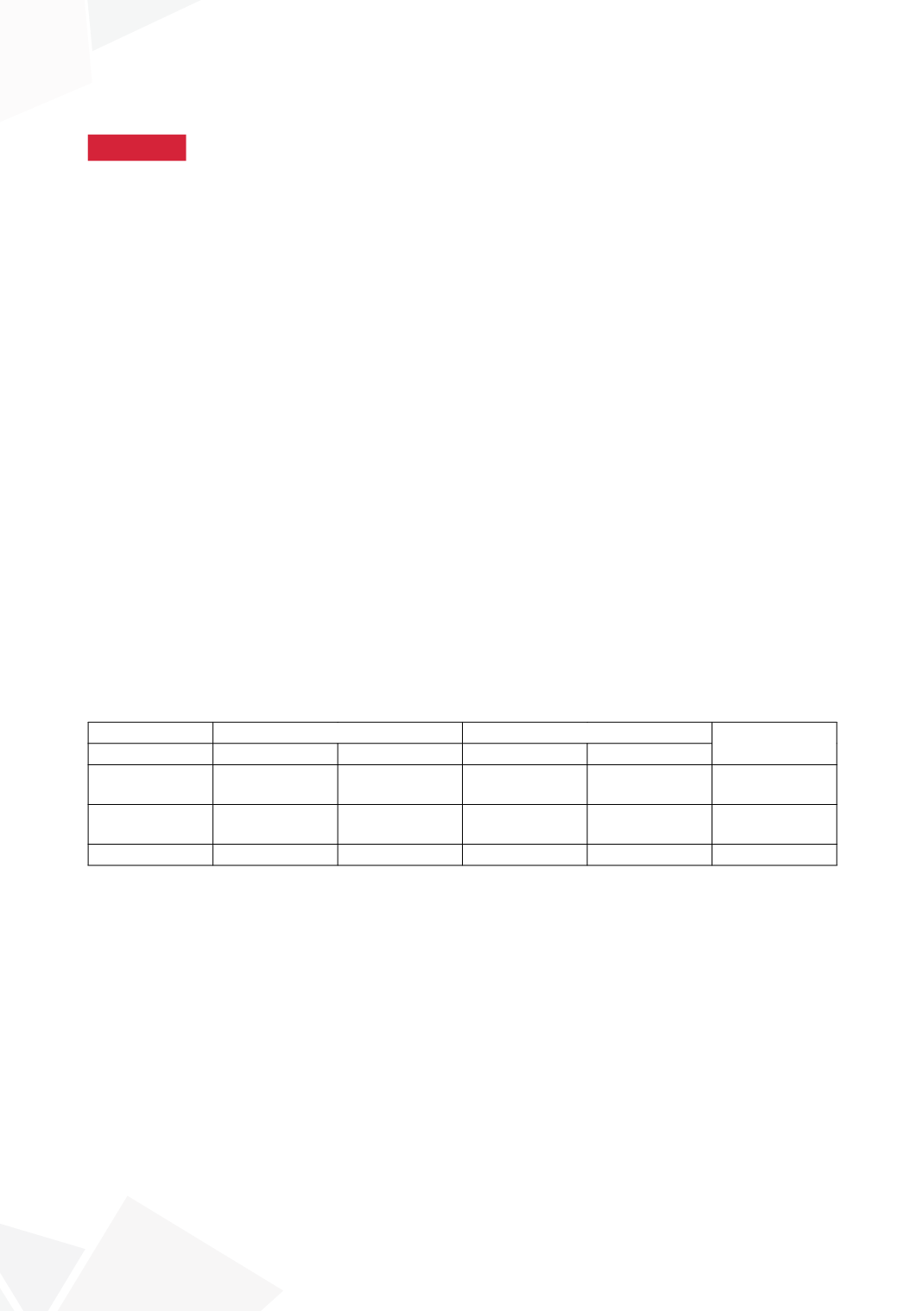
Decrease in arousal score and plasma BNP level, and increase in plasma ADH level were seen
in all post-surgery. However, mixed ANOVA showed that responders (dry) had significantly more
improvement than non-responders (wet) in the quality of sleep (Table). Following TA, nearly all
dry children reported nocturia and significant decrease in BNP levels (P=0.017) without significant
change in their NUV.
Dry (N=20)
Wet (N=20)
P-value
Pre-T&A
Post-T&A
Pre-T&A
Post-T&A
Heavy sleeper
Yes (%)
10 (50%)
2 (11.8%)
13 (27.8%)
16 (88.9%)
0.020
Snoring
Yes (%)
20 (100%)
3 (15.8%)
20 (100%)
7 (35.0%)
<0.001
Arousal score 13.17 ± 4.27 7.89 ± 5.04
9.64 ± 3.56
6.00 ± 3.16
<0.001
CONCLUSIONS
Change in children’s quality of sleep and arousal score was associated with NE resolution post-TA.
Improvement in sleep quality appears to be responsible for the effect of TA on NE in children with
SDB.









