
80
28
TH
CONGRESS OF THE ESPU
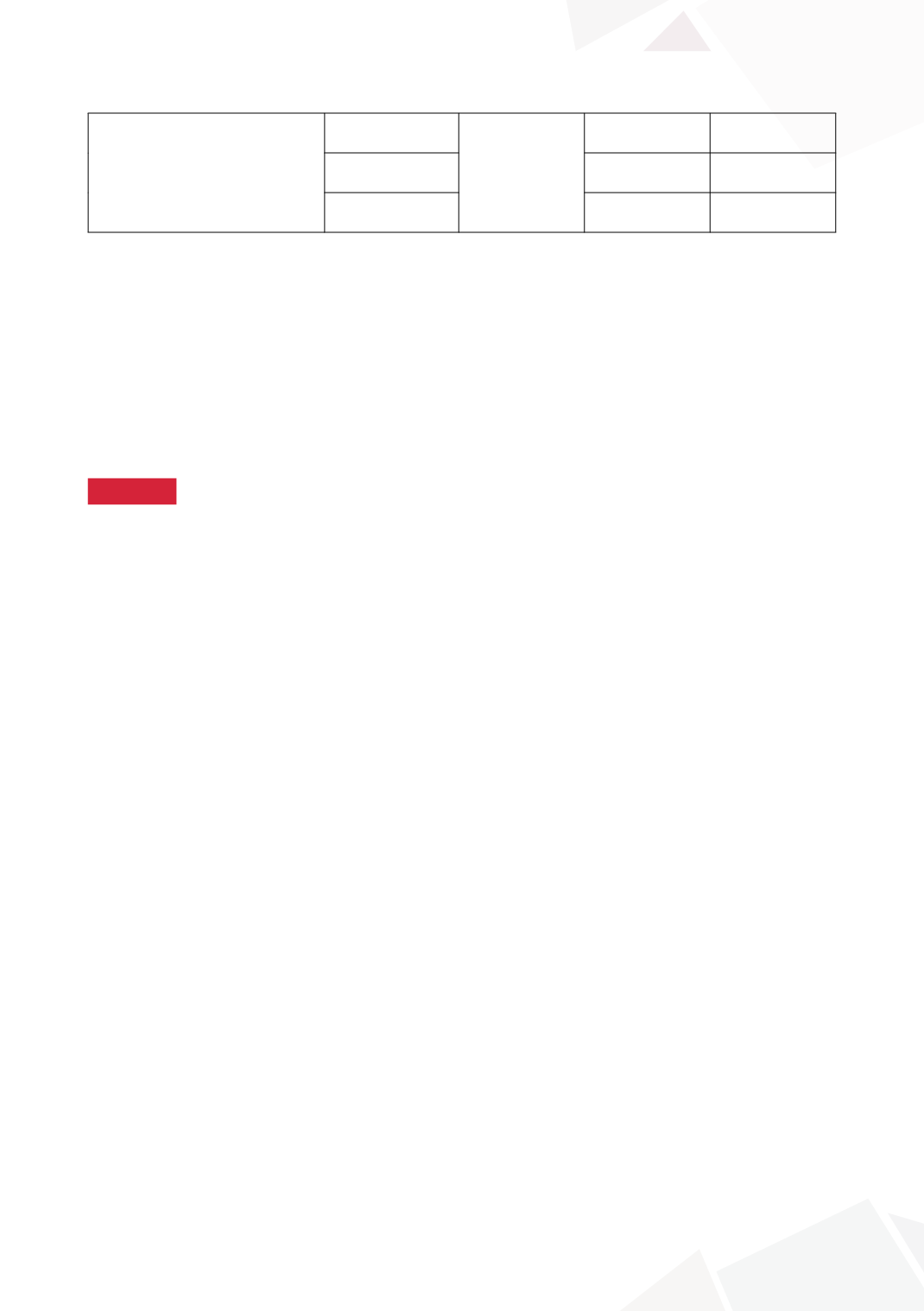
Number of patients with
histological features
Cystitis cystica /
glandularis
NA
21 (72%)
11 (85%)
Squamous
metaplasia
17 (59%)
6 (46%)
Intestinal
metaplasia
5* (17%)
8* (61%)
CONCLUSIONS
Intestinal metaplasia appears to be more prevalent in those with severely polypoid bladder tem-
plates. A careful strategy is needed for these patients to maximise the chance for successful BE
closure and the authors suggest polypectomy prior to BE closure. Polyp regrowth does not appear
to be a major problem as 5% required a second polypectomy prior to BE closure.
10:59–11:14
Discussion
11:14–11:17
S7-6 (PP)
COMPLETE PRIMARY REPAIR OF BLADDER EXSTROPHY:
A CONTEMPORARY SERIES WITH TIME TO EVENT
ANALYSIS
Tamer HELMY
1
, Hesham ORBAN
2
, Helmy OMAR
2
, Ahmed GALAL
2
, Ashraf HAFEZ
2
and Mohammed DAWABA
2
1) Urology & Nephrology center Mansoura, Paediatric Urology, El Mansoura, EGYPT - 2) Urology and Nephrology
Center, Paediatric Urology, Mansoura, EGYPT
PURPOSE
To report long term outcomes after complete primary repair of bladder exstrophy in a tertiary referral
center.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
we retrospectively reviewed the records of all patients who underwent classic bladder exstrophy
closure between June 1998 and May 2010. Patients who were subjected to complete primary repair
were filtered for further analysis. Data reviewed included demographic data, history of previous
attempts of closure, surgical technique; follow up after exstrophy closure; continence status, meas-
ures performed to achieve continence and status at last follow up.
RESULTS
This cohort included 43 boys and 15 girls. Previous attempts of closure were done in 28 children.
After 110 months, 2 achieved volational voiding. BNI was tried in 21. Two patients only were dry.
BNR with augmentation cystoplasty was performed in 36 children. 26 patients were dry. Continent
stoma was used for all patients after BNR. Bulbourethral sling was tried in 15 children (8 after
BNI-3 after BNR and 4 denovo patients). Three patients after BUS could achieve partial dryness.
Bladder neck transection was performed in 17 children (8 denovo patients, 7 after BNR and 2 after
BUS).
CONCLUSIONS
Long term results after complete primary repair were unsatisfactory and this in turn aborts the past
expectations of reduction of continence surgeries. Based on these dismal results, staged repair now
is considered the standard of care approach for our neonatal exstrophy babies.









