
61
19–22 APRIL, 2017, BARCELONA, SPAIN
MATERIAL AND METHODS
The data of 686 patients who were operated for VUR between 1997-2016 was analyzed retrospec-
tively. The results were analyzed with SPSS 17.0 software.
RESULTS
The mean age was 69.6±44 months (3-204), male to female ratio was 250/436. STING was per-
formed 42% of patients and ureteroneocyctostomy(UNC) was performed 58% of patients. Success
of STING was 75%, success of UNC was 93% (p<0.0001). Patients with previous STING history
which performed STING or UNC; both of procedure have lower succes rate (STING (%63 vs %77,
p=0.025; UNC %87 vs %94, p=0.024) . VD and VUR grade do not affect the success rate for the
each surgery groups. In patient with voiding dysfunction have low grade VUR, higher female and
STING ratio.
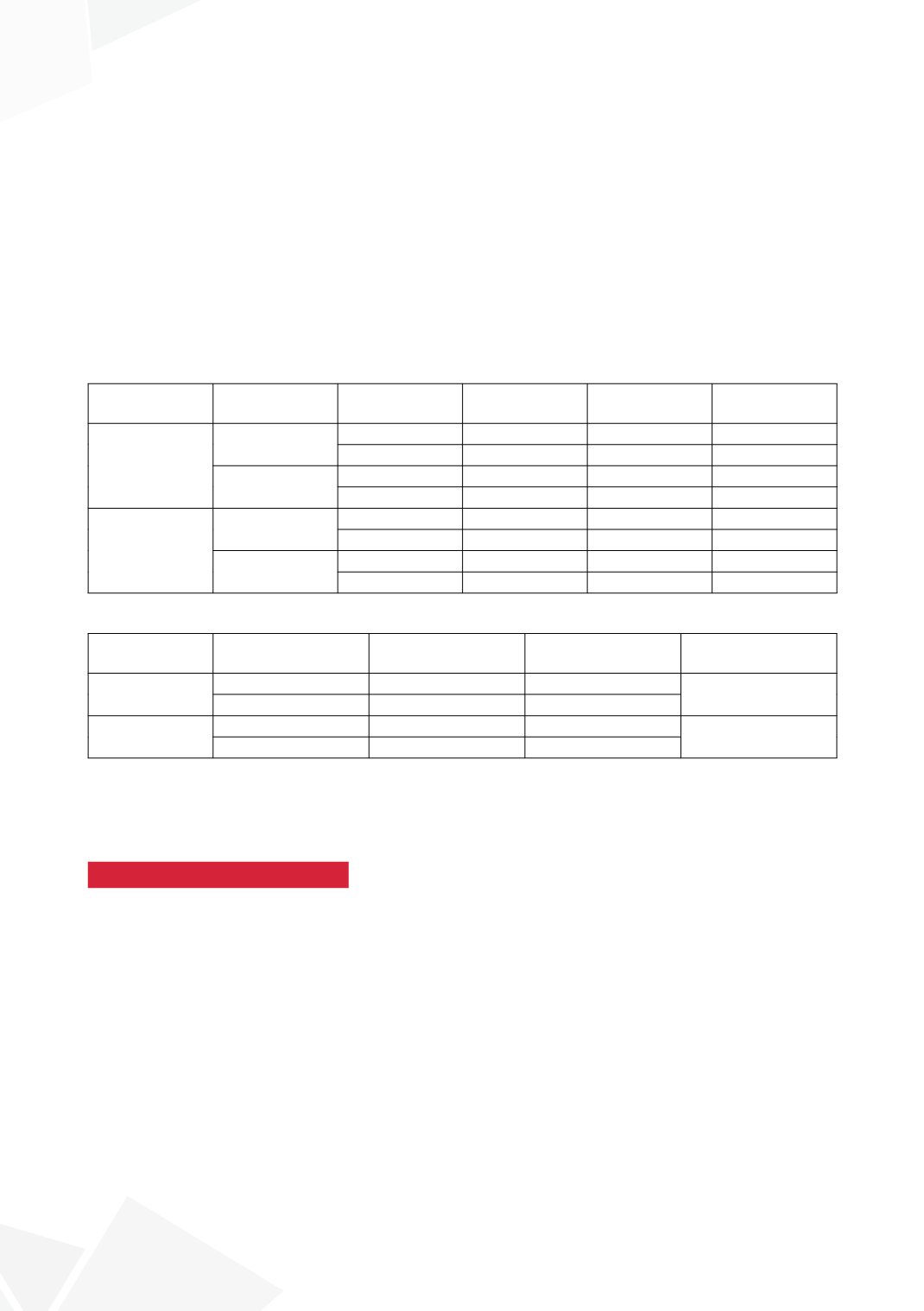
Table 1:
Operation
Preoperative
STING history
Voiding
disfunction
Successful
Unsuccessful
p
STING
No
No
58 (84%)
11
0.375
Yes
42(78%)
12
Yes
No
10 (71%)
4
0.383
Yes
6 (55%)
5
UNC
No
No
120 (94.5%)
7
0.220
Yes
41 (89%)
5
Yes
No
25 (83%)
5
1.000
Yes
6 (86%)
1
Table 2:
Operation
Previous STING
history
Success
Unsuccessful
p
STING
No
189 (77%)
54
0.025
Yes
30 (63%)
18
UNC
No
296 (94%)
18
0.024
Yes
66 (87%)
10
CONCLUSIONS
The success rate of patient with previous STING history is decreasing. VD and VUR grade do not
affect operation success.
S5-10 (P without presentation)
IS EAU/ESPU VUR RISK CLASSIFICATION COMPATIBLE
WITH CLINICAL PRACTICE?
Ali Cansu BOZACI, Burak CITAMAK, Mesut ALTAN, Burhan OZDEMIR,
Hakan Bahadir HABERAL, Hasan Serkan DOGAN and Serdar TEKGUL
Hacettepe University, Urology, Ankara, TURKEY
PURPOSE
To investigate whether the risk groups for patient selection in the surgical treatment of vesicoureteral
reflux (VUR) is compatible with clinical practice.









