
153
19–22 APRIL, 2017, BARCELONA, SPAIN
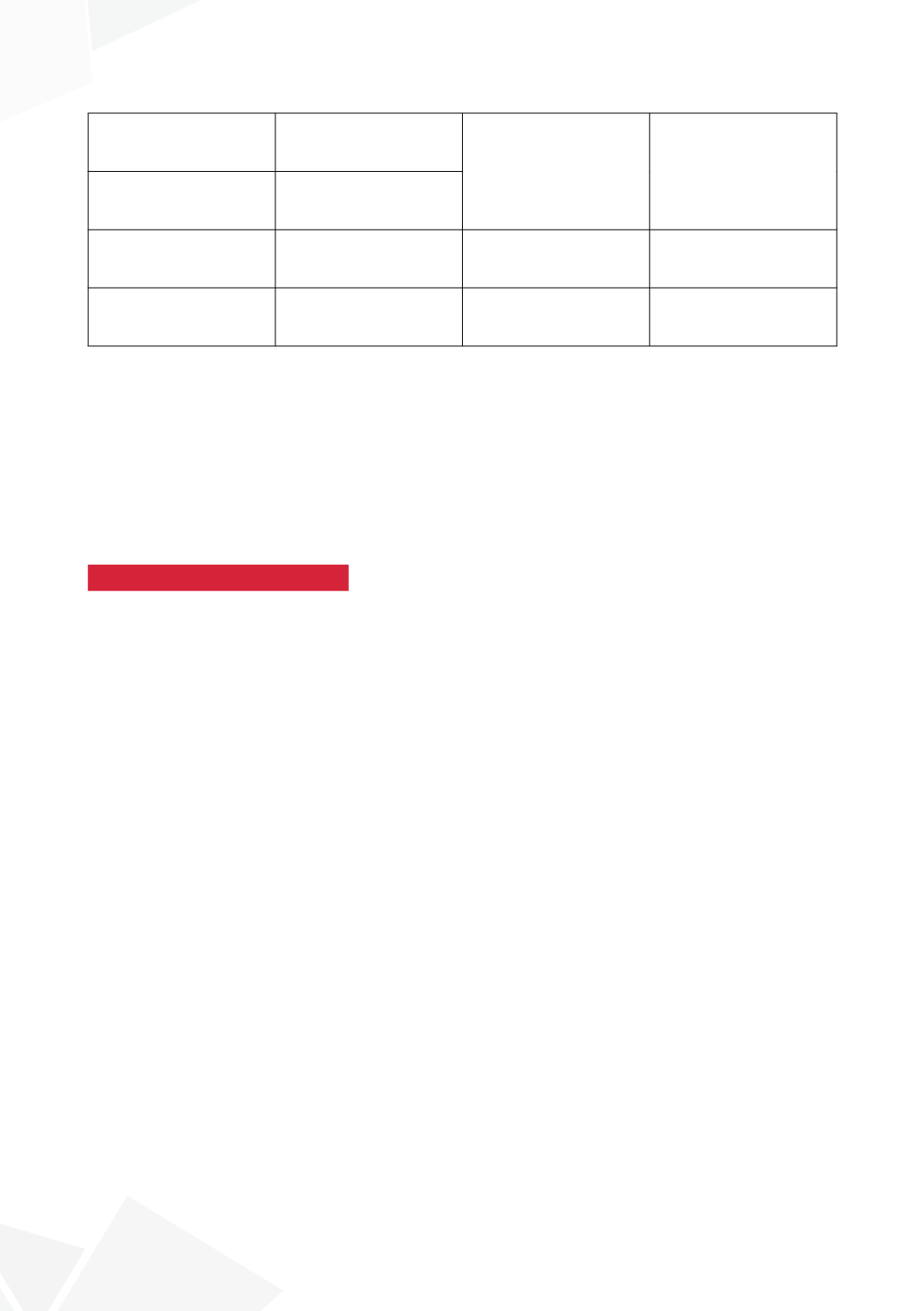
Glans Groove
Moderate/Deep
Absent/Shallow
16(8.4)
22(18.2)
2.8(1.3-6.1)
0.01
UP Quality
Robust Spongiosum
Poor Spongiosum
19(7.8)
19(27.9)
Anesthesia
Caudal
Dorsal Penile Block
35(13.2)
3(6.4)
2.2(0.6-7.4)
0.24
GMS Score(Surgery)
<7
≥7
18(8.5)
20(20.0)
1.6(0.7-3.9)
0.25
CONCLUSIONS
Previous literature has demonstrated an association between increased GMS scores and higher
complication rates. Although PTS reduced GMS scores at surgery, our findings suggested that
PTS, and the subsequent lower GMS score,did not significantly reduce postoperative complica-
tions. A combination of glans groove depth/UP quality was the main risk factor for TIP complications.
09:15–09:24
Discussion
S14-8 (P without presentation)
CORRELATION BETWEEN PENILE LENGTHS MEASURED
DURING SURGERY AND COMPLICATION RATES
IN HYPOSPADIAS
Halil TUGTEPE
1
, Raziye ERGUN
2
, David Terence THOMAS
3
, Tural ABDULLAYEV
4
and Tolga E. DAGLI
2
1) Marmara Un. Medical Faculty, Dep. of Ped. Surgery, Section of Pediatric Urology, Istanbul, TURKEY - 2) Marmara
University School of Medicine, Department of Pediatric Surgery, Division of Pediatric Urology, Istanbul, TURKEY -
3) Maltepe University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Pediatric Surgery, Istanbul, TURKEY - 4) Marmara University
School of Medicine, Department of Pediatric Surgery, Istanbul, TURKEY
PURPOSE
Decrease of complication rates is a primary aim in hypospadias surgery. A recent study found that
a glans diameter of under 14mm was an independent risk factor for he development of compli-
cations. In this study, our aim was to compare complication rates to penile lengths taken during
surgery for hypospadias.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Successive patients undergoing TIPU for hypospadias at our Pediatric Urology clinic between
February 2013 and March 2016 were prospectively included in this study. Patients with proximal
hypospadias, secondary cases and those undergoing two session repair were excluded. Patients’
age, meatus location, penile lenghts measured during surgery (penis length, penis stretch length,
glans diameter, ürethral plate width before and after incision), follow up times and complications
occuring during the followup period were noted. Penile lengths of those with complications and
those without, plus complication rates of patients with glans diameter above or below 14mm were
compared.









