
161
11–14 APRIL, 2018, HELSINKI, FINLAND
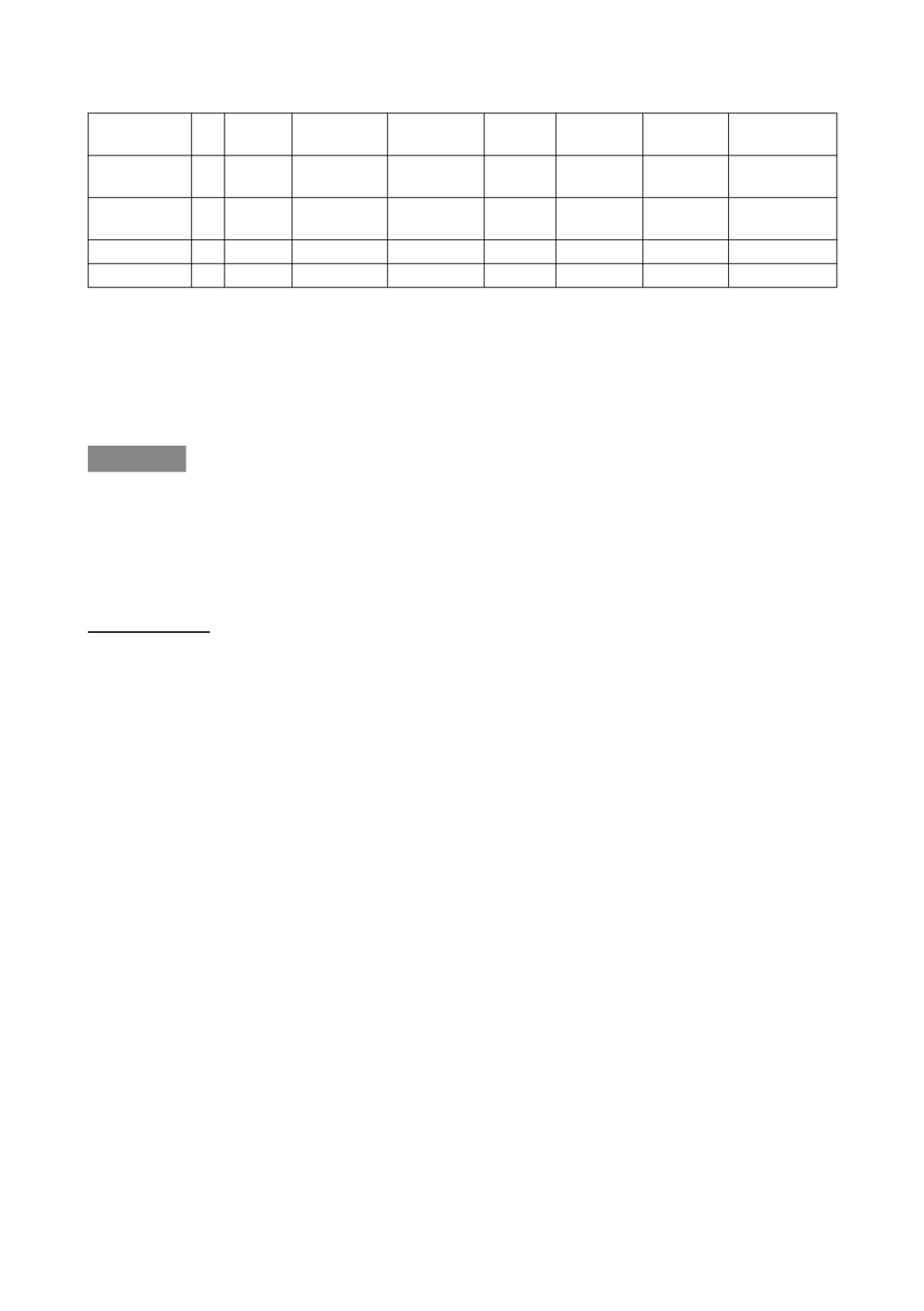
DIAGNOSIS N° UTI
ENURESIS URGENCY CREDE INCONTI
NENCE
BOWEL
DYS.
SELF-CARE
CP
30 13,3 %
60 % 33,3 % 23,3 %
26,6 %
53,3 % 52 %
ABI
17 23,5 % 58,8 %
35,2 % 35,3 % 11,7 % 64,7 % 54 %
SCI
3 66,6 % 100 % 33,3 % 66,6 % 33,3 % 33,3 % 43 %
OTHER 10 0 % 70 % 30 % 20 % 30 % 70 % 59 %
CONCLUSIONS
ABI is an heterogenous group of patients with vascular, oncological, traumatic brain injury. ICIQ is
a valid screener ABI for detecting BBD. BBD are present in ABI as in CP and we can consider BBD
a missed problem in ABI reclaiming major attention.
08:43–08:46
S21-7 (PP)
★
ASSESSMENT OF BLADDER COMPLIANCE
BY A PRESSURE ADJUSTED NEW PARAMETER:
A PROMISING TOOL TO PREDICT UPPER URINARY TRACT
CHANGES IN NEUROPATHIC BLADDER
Sibel TIRYAKI, Ali AVANOGLU and Ibrahim ULMAN
Ege University - Faculty of Medicine, Pediatric Surgery Division of Pediatric Urology, Izmir, TURKEY
PURPOSE
Compliance values are frequently inconclusive during urodynamic studies, thus detrusor leak point
pressure (DLPP) became the most reliable parameter in risk assessment for upper tract. Yet, the
duration of high pressure during filling phase rather than a single leak point value may better reflect
it. We hypothesized that a different calculation comparing the area under curve (AUC) to a DLPP-
adjusted total area can be more sensitive than classical repetitive measurement of compliance.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
A new parameter (PAUC) was derived from the proportion of AUC to a DLPP-adjusted total area
(A
T
). AUC was calculated from cystometrogram using ImageJ software. A
T
was computed from
a rectangle formed on graph with a fixed height of 200 cmH
2
O to include all DLPP values and
a width defined by the filling phase. After calculation of PAUC from two different urodynamic studies
with an interval of >5 years, files of 91 myelomeningocele patients with imaging studies (ultrasonog-
raphy and scintigraphy) performed at the time of urodynamics were retrospectively reviewed. The
powers of PAUC, DLPP, compliance, and volume in predicting upper tract changes were evaluated
using ROC analysis.
RESULTS
PAUC amongst all had the best discrimination in predicting urinary tract dilatation (UTD) (table).
A value of 0.06 was a significant cut-off value (sensitivity 0.75, specificity 0.41, PPV%75, NPV%56).
PAUC>0.06 significantly correlated with UTD (p<0.001) and new scar formation (p=0.01).











