
146
29
th
CONGRESS OF THE ESPU
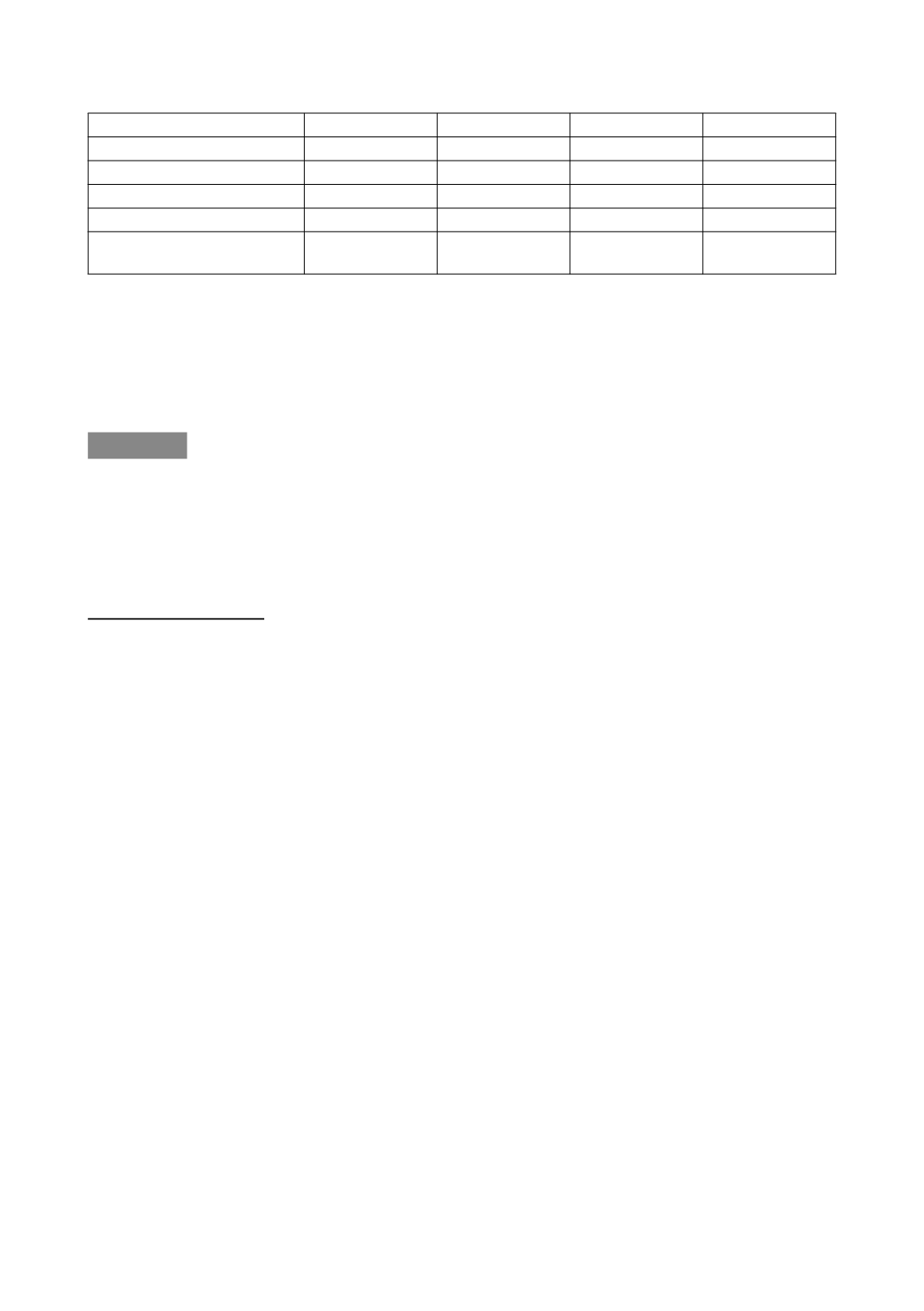
Characteristic/outcome
5 y (n=50)
10 y (n=54)
15 y (n=29)
p
Incomplete emptying
64 % (n=32)
54 % (n=29)
62 % (n=18)
0.5350
LUTS
34 % (n=17)
33 % (n=18)
14 % (n=4)
0.1152
Anticholinergics/CIC
26 % (n=13)
22 % (n=12)
10 % (n=3)
0.2489
Abnormal uroflow
40 % (n=20)
33 % (n=18)
38 % (n=11)
p=0.7730
Any abnormal feature; one
or more of above
92 % (n=46)
87 % (n=46)
76 % (n=22)
0.1405
CONCLUSIONS
Bladder function in PUV is abnormal from childhood to puberty with no significant change in the
proportion of patients related to capacity, LUTS, need for treatment and uroflow.
1 Austin PF et al. J Urol 2014; 191: 1863–1865
16:03–16:08
S19-5 (LO)
[PRESENTATION GROUPED WITH PREVIOUS] IS BLADDER
CAPACITY IN POSTERIOR URETHRAL VALVES (PUV)
AT 5, 10 AND 15 YEARS ASSOCIATED WITH EMPTYING
AND RENAL IMPAIRMENT?
Riccardo MANUELE
1
, Joanna CLOTHIER
1
, Anne WRIGHT
1
, Vanessa GUIDI
2
, Aurora
MARIANI
2
, Kalpana PATIL
2
, Arash TAGHIZADEH
2
and Massimo GARRIBOLI
2
1) Evelina London Children's Hospital, Paediatric Bladder Disorders, London, UNITED KINGDOM - 2) Evelina London
Children's Hospital, Paediatric Urology, London, UNITED KINGDOM
PURPOSE
Bladder capacity (BC) in PUV may be abnormal; we studied whether BC is associated with incom-
plete emptying or impaired renal function.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
Retrospective cross-sectional review of non-invasive urodynamics at the age of 5, 10 and 15 years
in boys with PUV.
Data recorded: Bladder capacity (BC) classified as large, normal and small as per ICCS criteria1;
percentage ratio for BC and expected BC (EBC); post-void residuals (PVR); iohexol GFR.
Patients divided into 3 groups according to their age.
Statistical tests performed within each group (p statistically significant <0.01):
Chi Square to evaluate BC and incomplete emptying.
Pearson to compare voided volume (VV) and PVR
Pearson to compare BC/EBC% and GFR.
RESULTS
We identified studies from 133 children between 2008–2017; patients with renal transplant (n = 25)
and bladder augmentation (n = 13) were excluded.
There is no statistically significant correlation between incomplete bladder emptying and BC in the
three age groups (although there appears to be a trend); p=0.10, p=0.08, p=0.05.
VV is not related to PVR: p=0.30 (group 1), p=0.66 (group 2), p=0.48 (group 3).
Furthermore BC does not predict renal impairment: p=0.28 (group 1); p=0.64 (group 2);
p=0.31 (group 3).











